Welcome
Getting Started
How to Guides
Application vs Blocklet
Create Blocklet
Compose Blocklets
Develop Blocklet
User and Passport
Communicate with DID Wallet
Blocklet Storage
Using Blocklet Preferences
Using Blocklet Logger
Add PWA Integration to Blocklet
Build blocklet for profit [deprecated]
Bundle your blocklet
Manage Blocklet Versions
Publish your blocklet to the world
Deploy your blocklet
Read/Write blockchain in blocklet
Operation your blocklet
Reference Guides
DID Connect
blocklet.yml
blocklet.js
Blocklet SDK (Node.js)
Blocklet SDK (Browser)
Blocklet Service
Blocklet CLI
Blocklet Server CLI
Blocklet UI
Blocklet GitHub Actions
Blocklet Studio
Blocklet Manager
Security
Performance
Image Service
Theming
Developer Best Practices.
Known Issues or Limitations
Setup Blocklet Server
WebHooks
OAuth Server
Access Key
MCP Servers
Conceptual Guides
Frequently Asked Questions
How to configure security rules
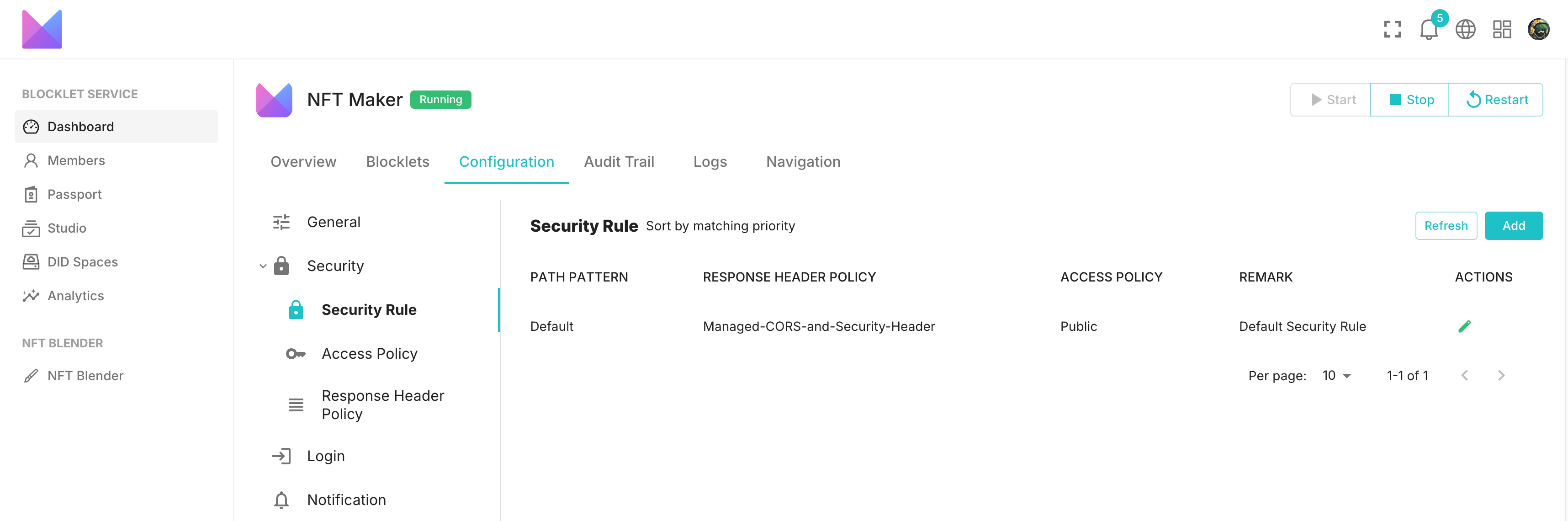
Overview of Security Rules#
Security rules are used to constrain external requests to the application, ensuring that only requests that meet certain criteria can access the application's resources. Each application's owner or administrator can configure these rules in the application console:
The security rules are primarily composed of three parts:
- Path Pattern: Requests are grouped and matched based on the URL, with only those requests that meet this pattern being subject to this rule (Default can match any URL).
- Response header policy: A unified approach to adding custom headers in response to requests based on security requirements.
- Access Policy: Specifies who can access the application.
Additionally, multiple security rules will match requests in a top-down order. If a rule is triggered, subsequent matching processes will be skipped.
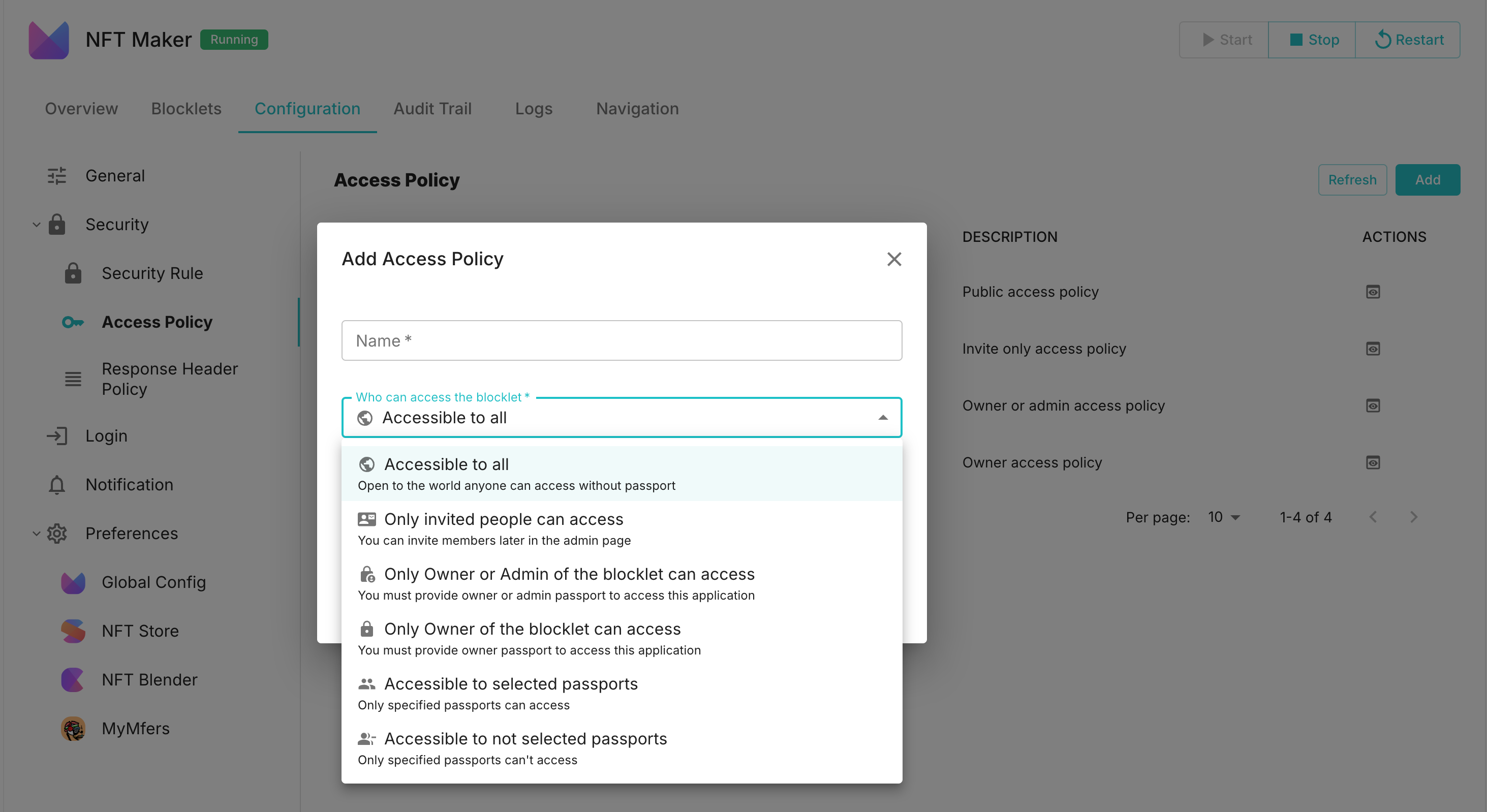
Access Policy#
Access policies can control who can access the application based on whether the user is logged in and their role, with specific options illustrated in the image below (if certain terms are unclear, you can refer to User and Passport):
Response Header Policy#
The response header policy is used to add necessary security headers to responses, controlling browser behavior and ensuring that the application meets security requirements.
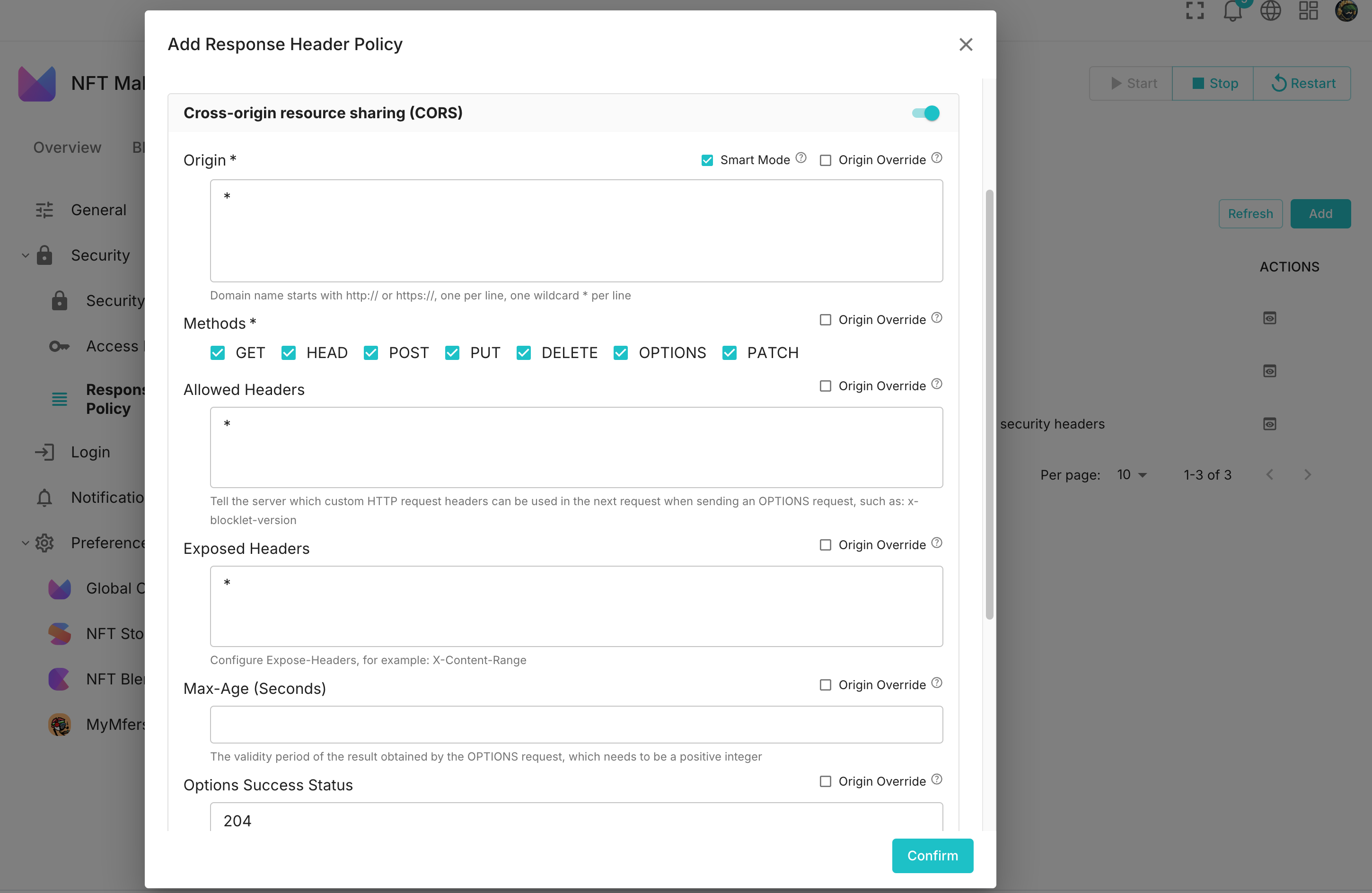
CORS Configuration#
CORS configuration allows control over which domains can access application resources, preventing malicious cross-origin requests. The main configuration options include:
- Origin: Specifies which source domains are permitted to make cross-origin requests. For instance, you can specify that cross-origin access is allowed from
https://example.com. - Methods: Allowed HTTP methods include
GET,POST,PUT,DELETE, and others. - Allowed Headers: A list of permitted request headers that specifies which headers can be sent in cross-origin requests.
- Exposed Headers: Response headers that are accessible to clients.
- Max Age: Specifies the validity period of the preflight request in seconds, indicating that the browser does not need to send preflight requests within this time frame.
- Options Success Status: Specifies the success status code for the preflight request, defaulting to
204. - Preflight Continue: Indicates whether to allow the continuation of the preflight request process.
- Credentials: Whether to allow cross-origin requests to include credentials (such as cookies).
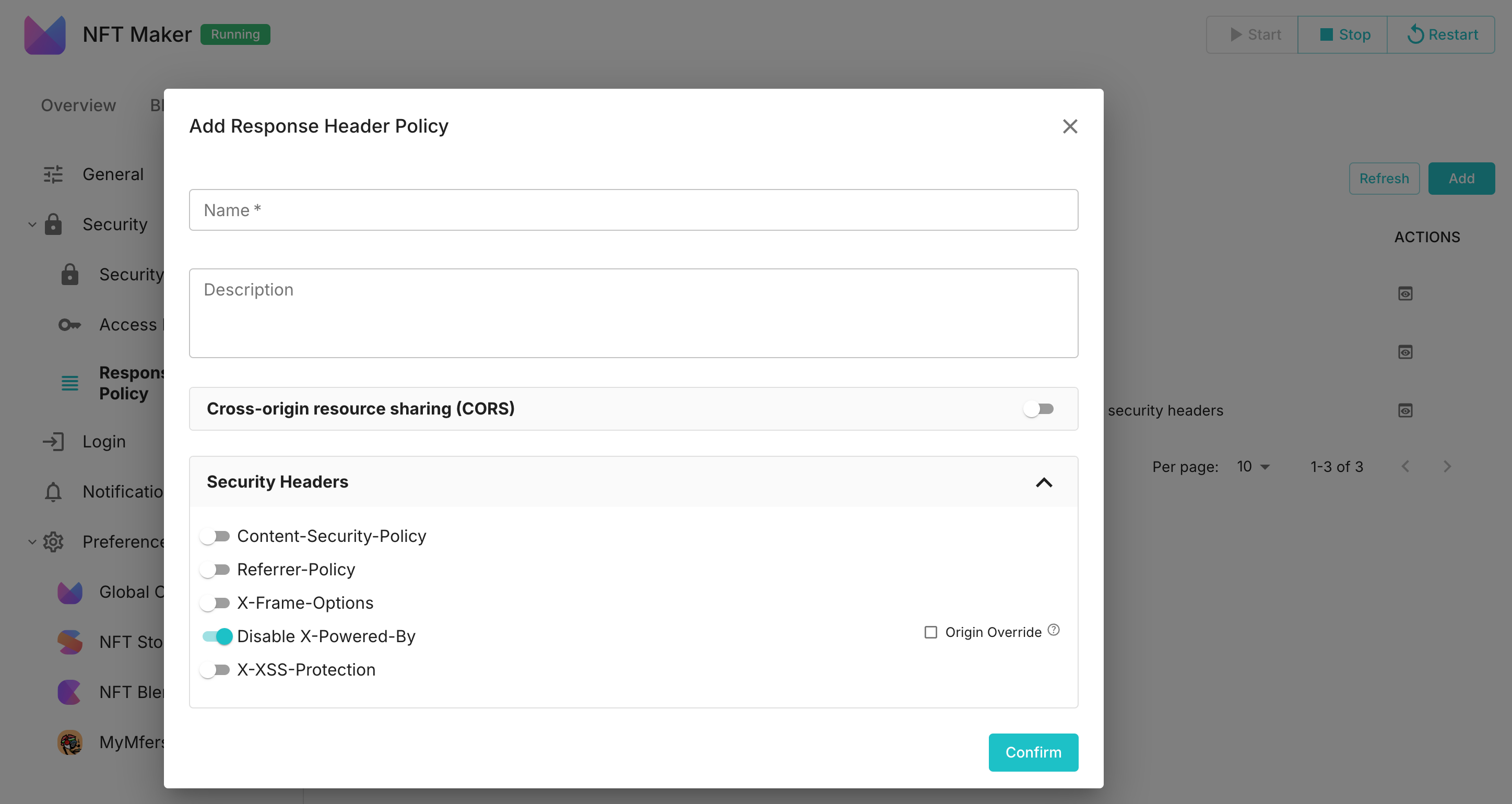
Security Header Configuration#
Security headers are configured to enhance the security of HTTP responses and to prevent common types of attacks. The main configuration items include:
- Content-Security-Policy (CSP): Used to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks and other code injection attacks by limiting the sources from which resources can be loaded (specific options can be found in the CSP Reference).
- Referrer-Policy: controls how the
Refererheader is sent, preventing the leakage of sensitive information (for specific options, refer to the Referrer Policy Reference). - X-Frame-Options: This header prevents webpages from being embedded within iframes, thus avoiding clickjacking attacks. Common values include
DENYandSAMEORIGIN. - Disable X-Powered-By: This prevents the exposure of server information, such as
X-Powered-By: Express, which could be exploited by attackers. - X-XSS-Protection: Prevents cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. A common value is
1; mode=block, indicating that XSS protection is enabled and page rendering is blocked.
FAQ#
What should I do if a request is blocked by CORS?#
If you encounter CORS issues, it is usually because the application has restrictions on cross-origin requests. You need to modify the CORS configuration in the application's backend response header policy by adding a whitelist or setting it to *.
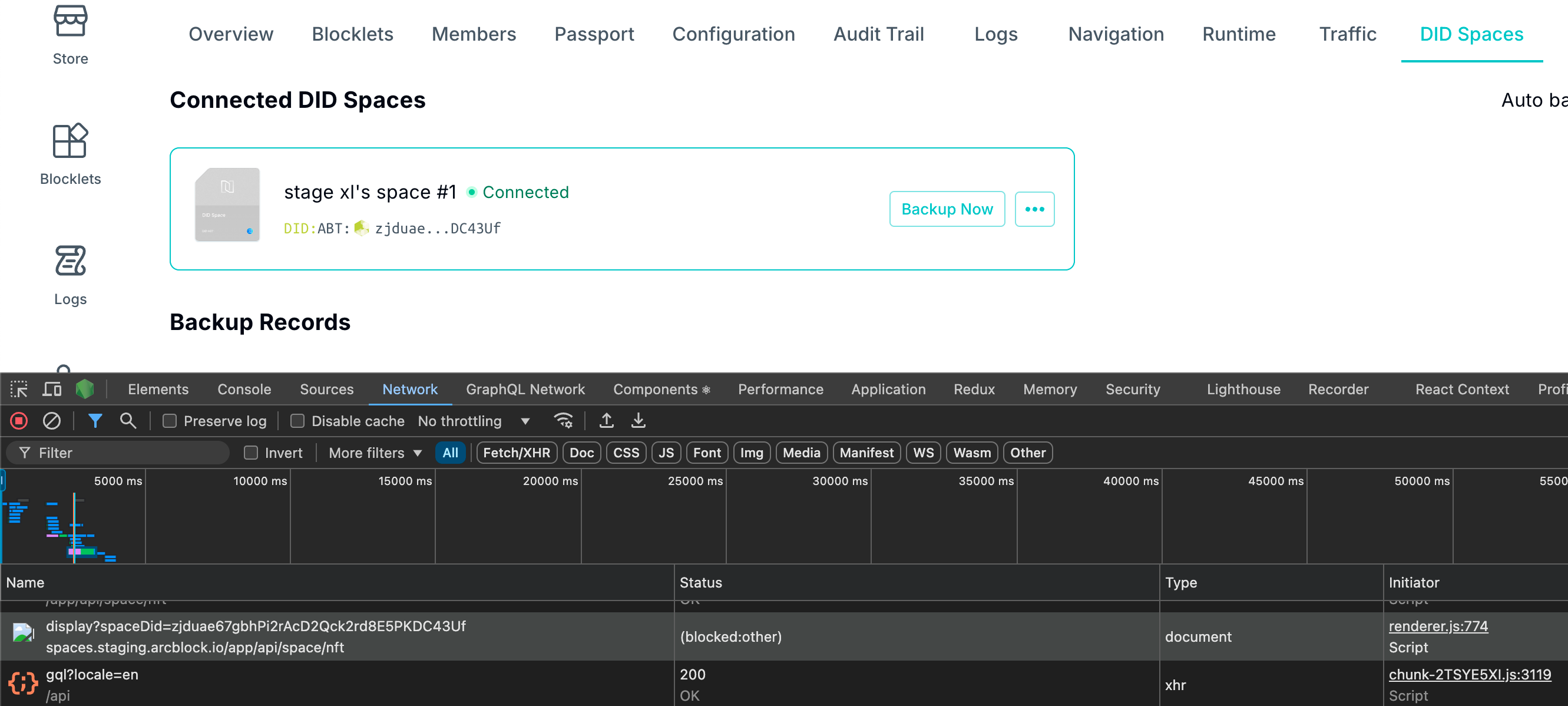
Why can't the NFT be previewed?#
For example, the NFT of the Space card shows blank:
The reason is that the default rules for Staging DID Spaces only allow NFT previews through the /app/resolve/display path, while Space cards preview NFTs through the /app/api/space/nft/display path:
Therefore, to address the issue of previewing NFTs on Space cards, a rule needs to be added to the /app/api/space/nft/display path:
Afterwards, the Space card will be able to display NFTs normally: