Workflow Orchestration
This guide demonstrates how to build and run a sophisticated workflow that orchestrates multiple specialized AI agents. You will learn to coordinate agents like a finder, writer, and proofreader to work together on a complex task, from initial research to final report generation.
Overview#
Workflow orchestration involves creating a processing pipeline where multiple agents collaborate to achieve a common goal. Each agent in the pipeline has a specific role, and a central orchestrator manages the flow of tasks and information between them. This example showcases how to use the AIGNE Framework to build such a system, supporting both single-run (one-shot) and interactive chat modes.
The following diagram illustrates the agent relationships in this example:
direction: down
User: {
shape: c4-person
}
OrchestratorAgent: {
label: "Orchestrator Agent"
shape: rectangle
finder: {
label: "Finder Agent"
shape: rectangle
}
writer: {
label: "Writer Agent"
shape: rectangle
}
}
Skills: {
label: "Skills / Tools"
shape: rectangle
style: {See all 20 lines
Prerequisites#
Before you begin, ensure you have the following installed and configured:
- Node.js: Version 20.0 or higher.
- npm: Comes bundled with Node.js.
- OpenAI API Key: Required for the agents to interact with OpenAI models. You can obtain one from the OpenAI Platform.
Optional dependencies for running from source code:
- Bun: For running unit tests and examples.
- Pnpm: For package management.
Quick Start#
You can run this example directly without any installation using npx.
Run the Example#
Execute the following commands in your terminal:
Run in one-shot mode
# Run in one-shot mode (default)
npx -y @aigne/example-workflow-orchestratorRun in interactive chat mode
# Run in interactive chat mode
npx -y @aigne/example-workflow-orchestrator --interactiveUse pipeline input
# Use pipeline input
echo "Research ArcBlock and compile a report about their products and architecture" | npx -y @aigne/example-workflow-orchestratorConnect to an AI Model#
The first time you run the example, it will prompt you to connect to an AI model service since no API keys have been configured.
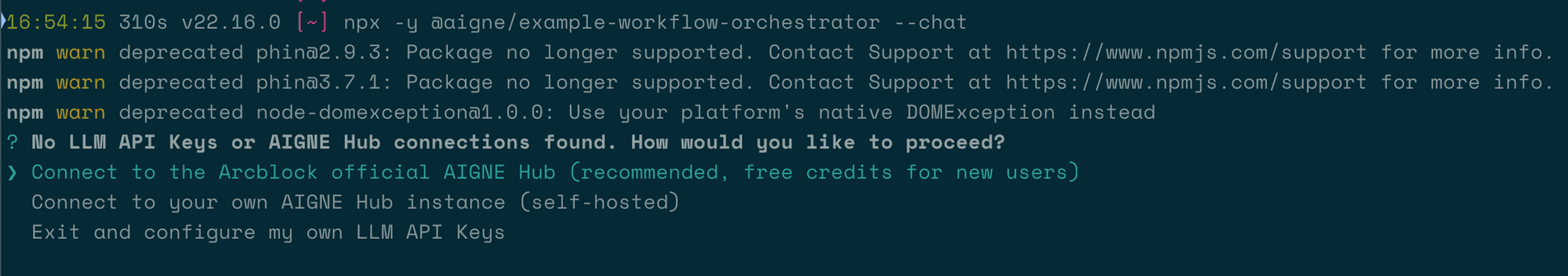
You have three options:
- Connect via the Official AIGNE Hub: This is the recommended option for new users. Selecting it will open your browser to an authorization page. After you approve, the CLI will be connected to the AIGNE Hub, and you'll receive complimentary tokens to get started.

- Connect via a Self-Hosted AIGNE Hub: Choose this if you have your own AIGNE Hub instance. You will be prompted to enter the URL of your hub to complete the connection. You can deploy a self-hosted AIGNE Hub from the Blocklet Store.

- Connect via a Third-Party Model Provider: You can configure an API key from a provider like OpenAI directly. Set the key as an environment variable and run the example again.
Set OpenAI API Key
export OPENAI_API_KEY="YOUR_API_KEY_HERE"
For more configuration examples, refer to the.env.local.examplefile in the repository.
Debugging with AIGNE Observe#
The aigne observe command launches a local web server that helps you monitor and analyze agent executions. This tool is invaluable for debugging, tuning performance, and understanding agent behavior.
First, start the observation server:
Start the observability server
aigne observe
Once the server is running, you can open the provided URL (http://localhost:7893) in your browser to view a list of recent agent traces and inspect their details.

Local Installation and Usage#
For development purposes, you can clone the repository and run the example locally.
1. Clone the Repository#
Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/AIGNE-io/aigne-framework2. Install Dependencies#
Navigate to the example directory and install the necessary packages using pnpm.
Install dependencies
cd aigne-framework/examples/workflow-orchestrator
pnpm install3. Run the Example#
Use the pnpm start command to execute the workflow.
Run in one-shot mode
# Run in one-shot mode (default)
pnpm startRun in interactive chat mode
# Run in interactive chat mode
pnpm start -- --interactiveUse pipeline input
# Use pipeline input
echo "Research ArcBlock and compile a report about their products and architecture" | pnpm startRun Options#
The script accepts several command-line parameters to customize its behavior.
Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Run in interactive chat mode. | Disabled |
| Specify the AI model to use (e.g., |
|
| Set the temperature for model generation. | Provider default |
| Set the top-p sampling value. | Provider default |
| Set the presence penalty value. | Provider default |
| Set the frequency penalty value. | Provider default |
| Set the logging level (e.g., |
|
| Specify input directly via the command line. | None |
Examples#
Run in interactive chat mode
# Run in chat mode
pnpm start -- --interactiveSet a different logging level
# Set logging level to DEBUG
pnpm start -- --log-level DEBUGCode Example#
The following TypeScript code demonstrates how to define and orchestrate multiple agents to perform in-depth research and compile a report. The OrchestratorAgent coordinates a finder and a writer, which are equipped with skills to browse the web (puppeteer) and interact with the local filesystem.
orchestrator.ts
import { OrchestratorAgent } from "@aigne/agent-library/orchestrator/index.js";
import { AIAgent, AIGNE, MCPAgent } from "@aigne/core";
import { OpenAIChatModel } from "@aigne/core/models/openai-chat-model.js";
const { OPENAI_API_KEY } = process.env;
// 1. Initialize the chat model
const model = new OpenAIChatModel({
apiKey: OPENAI_API_KEY,
modelOptions: {
parallelToolCalls: false, // Puppeteer can only run one task at a time
},
});
// 2. Set up MCP agents for web scraping and filesystem access
const puppeteer = await MCPAgent.from({
command: "npx",
args: ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-puppeteer"],
env: process.env as Record<string, string>,
});
const filesystem = await MCPAgent.from({
command: "npx",
args: ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem", import.meta.dir],
});See all 49 lines
When executed, this workflow produces a detailed markdown file. You can view an example of the generated output here: arcblock-deep-research.md.
Summary#
This example illustrates the power of the AIGNE Framework for building complex, multi-agent workflows. By defining specialized agents and coordinating them with an orchestrator, you can automate sophisticated tasks that require multiple steps, such as research, content generation, and file manipulation.
For more examples of advanced workflow patterns, explore the following sections: