Delegated Connect
Delegated Connect is an advanced feature that enhances security by allowing an application to perform DID Connect operations using a temporary or lower-privilege "agent" DID, while still presenting its primary, official DID to the end-user. This means the application's main private key is never exposed in the hot wallet that handles day-to-day interactions.
This guide explains the concept of Delegated Connect and shows how to implement it using WalletAuthenticator.
How It Works#
Delegated Connect involves three key participants:
- Delegator: The primary DID that owns the application's identity. This is the DID that users will see and trust. The delegator's wallet holds the main private key, which should be kept in secure, cold storage.
- Agent: A secondary, temporary DID that is authorized to act on behalf of the delegator for specific DID Connect operations. The agent's wallet is used by the application backend to sign authentication requests.
- Delegation Certificate: A Verifiable Credential, formatted as a JWT, signed by the Delegator. This certificate cryptographically proves that the Agent has permission to act for the Delegator. It typically includes an expiration time and a list of permitted claims.
The process ensures that even if the agent's key is compromised, the damage is limited by the permissions and expiration date defined in the delegation certificate. The delegator's primary key remains secure.
The Flow#
Here is a diagram illustrating the delegated authentication flow:
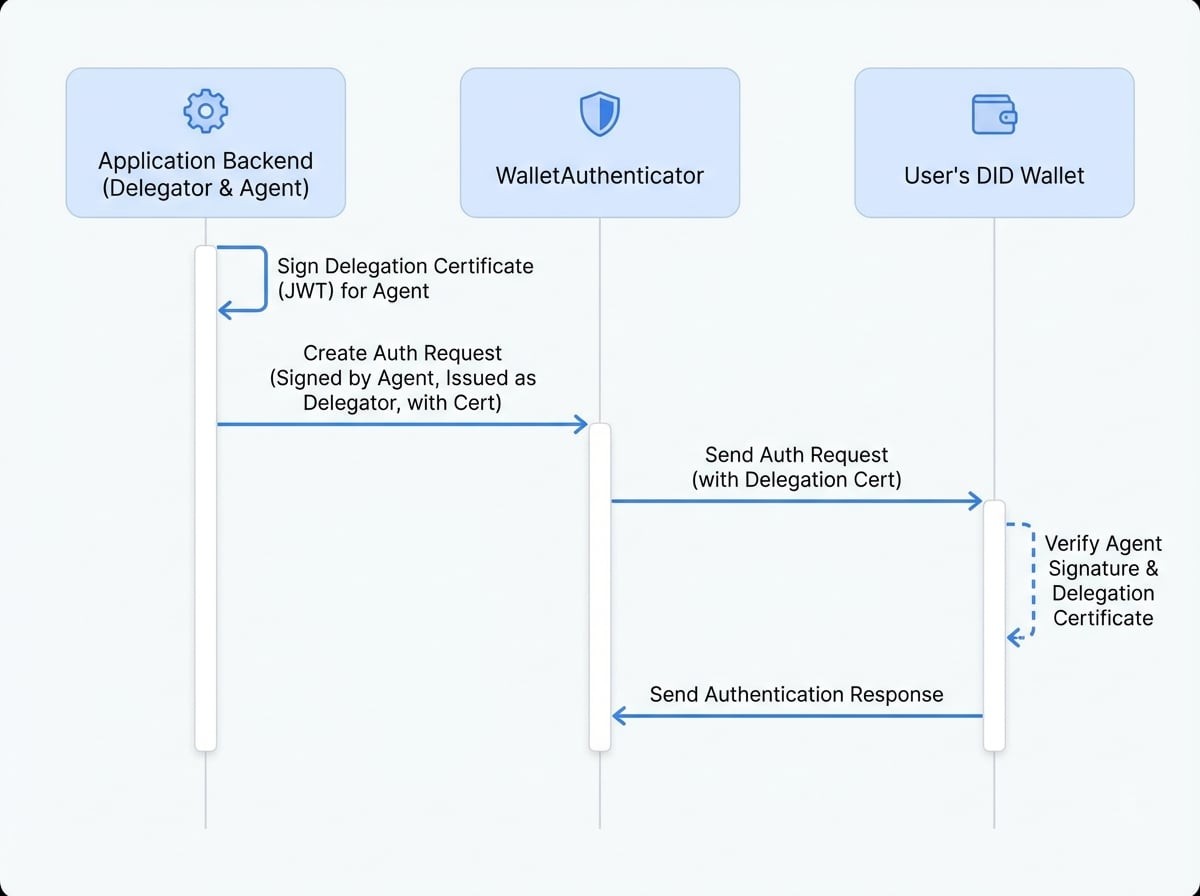
- Delegation: The Delegator signs a JWT that grants the Agent permission to perform DID Connect actions.
- Request: The application's
WalletAuthenticatorcreates an authentication request. It's signed by the Agent, but theiss(issuer) field is set to the Delegator's DID. The request also includes the Delegation Certificate. - Verification: The user's wallet receives the request. It first verifies the message signature using the Agent's public key. Then, it verifies the included Delegation Certificate using the Delegator's public key. This two-step process confirms the agent's authority.
- Response: The user approves the request, which clearly shows the Delegator's identity, and the wallet sends the response back to the application.
Implementation#
To implement Delegated Connect, you need to configure the WalletAuthenticator with the delegator, the agent wallet, and the delegation certificate.
Step 1: Define Delegator and Agent#
First, you need two distinct wallets. One will serve as the delegator (the main identity) and the other as the agent (the active signer).
Wallet Setup
const { fromRandom } = require('@ocap/wallet');
// The primary, trusted identity of your application
const delegator = fromRandom();
// The agent wallet that will handle daily operations
const agent = fromRandom();Step 2: Create the Delegation Certificate#
The certificate is a JWT signed by the delegator, granting permissions to the agent.
Create Delegation JWT
const Jwt = require('@arcblock/jwt');
const { toDid } = require('@ocap/util');
const createDelegation = async () => {
const now = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);
const claims = [
'authPrincipal',
'profile',
'signature',
'prepareTx',
'agreement',
'verifiableCredential',
'asset',
'keyPair',
'encryptionKey',
];
const payload = {
agentDid: toDid(agent.address),
permissions: [
{
role: 'DIDConnectAgent',
claims: claims,
},
],See all 9 lines
Step 3: Configure WalletAuthenticator#
Instantiate WalletAuthenticator by providing the delegator, the delegation certificate, and the wallet (which is the agent).
Authenticator Configuration
const { WalletAuthenticator, WalletHandlers } = require('@arcblock/did-connect');
const MemoryAuthStorage = require('@arcblock/did-connect-storage-memory');
const authenticator = new WalletAuthenticator({
// The 'wallet' property is our AGENT
wallet: () => agent.toJSON(),
// The delegator is the main app identity
delegator: () => delegator.toJSON(),
// The JWT proving the delegation
delegation: () => delegationCert,
appInfo: () => ({
name: 'Delegated Connect Demo',
description: 'Demo of delegated authentication',
icon: 'https://arcblock.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/images/wallet-round.png',
}),
});
const handlers = new WalletHandlers({
tokenStorage: new MemoryAuthStorage(),
authenticator,
});
See all 11 lines
When the DID Connect session starts, the WalletAuthenticator will automatically handle the delegated flow. The QR code will contain the necessary information for the user's wallet to verify the chain of trust from the delegator to the agent. The user will see a request from your application's main identity (the delegator), providing a seamless and secure experience.
For more details on the constructor options, see the WalletAuthenticator API Reference.