Core Concepts
This section explains the fundamental concepts behind ArcBlock's Decentralized Identity (DID). A DID in the ArcBlock ecosystem is more than just an identifier; it's a self-contained, self-describing entity that embeds its own cryptographic properties. This design allows for a versatile and interoperable identity system.
DID Structure#
An ArcBlock DID is a string that follows the W3C DID specification format, prefixed with did:abt:. The part that follows the prefix is a Base58 encoded string that contains all the necessary information about the identity.
For example: did:abt:zNKoDmH82m9fW5n444z4T8tWz9t2v7q3m6s
The core of the DID is a 26-byte buffer that contains:
- Type Information (2 bytes): Encodes the cryptographic suite used by the DID.
- Public Key Hash (20 bytes): A hash of the public key associated with the DID.
- Checksum (4 bytes): Ensures the integrity of the DID string.
This structure makes ArcBlock DIDs self-validating and self-describing, as you can derive the DID's capabilities directly from the DID string itself.
The DIDType Object#
The DIDType object is a crucial configuration object that defines the cryptographic characteristics of a DID. It specifies the algorithms used for key pairs, hashing, and address encoding.
Specifies the purpose or role of the DID. Different roles may have different cryptographic requirements. For example, a ROLE_NODE uses SHA2 for hashing, while a ROLE_ACCOUNT uses SHA3. Common roles include ROLE_ACCOUNT, ROLE_APPLICATION, ROLE_NODE, and ROLE_PASSKEY.
Defines the public key cryptography scheme used for signing and verification. Supported types include ED25519, ETHEREUM, and PASSKEY.
Specifies the hashing algorithm used to generate the public key hash and the checksum. Supported algorithms include SHA3, SHA2, and KECCAK.
Determines the encoding format of the final DID address string. The primary formats are BASE58 (for standard ArcBlock DIDs) and BASE16 (for Ethereum-compatible DIDs).
DID Type Presets#
To simplify DID creation, the library provides several string shortcuts that correspond to pre-configured DIDType objects for common use cases.
Shortcut | Role | Key Type | Hash Type | Encoding | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| Standard user and application accounts. |
|
|
|
|
| Ethereum-compatible accounts. |
|
|
|
|
| DIDs managed by WebAuthn Passkeys. |
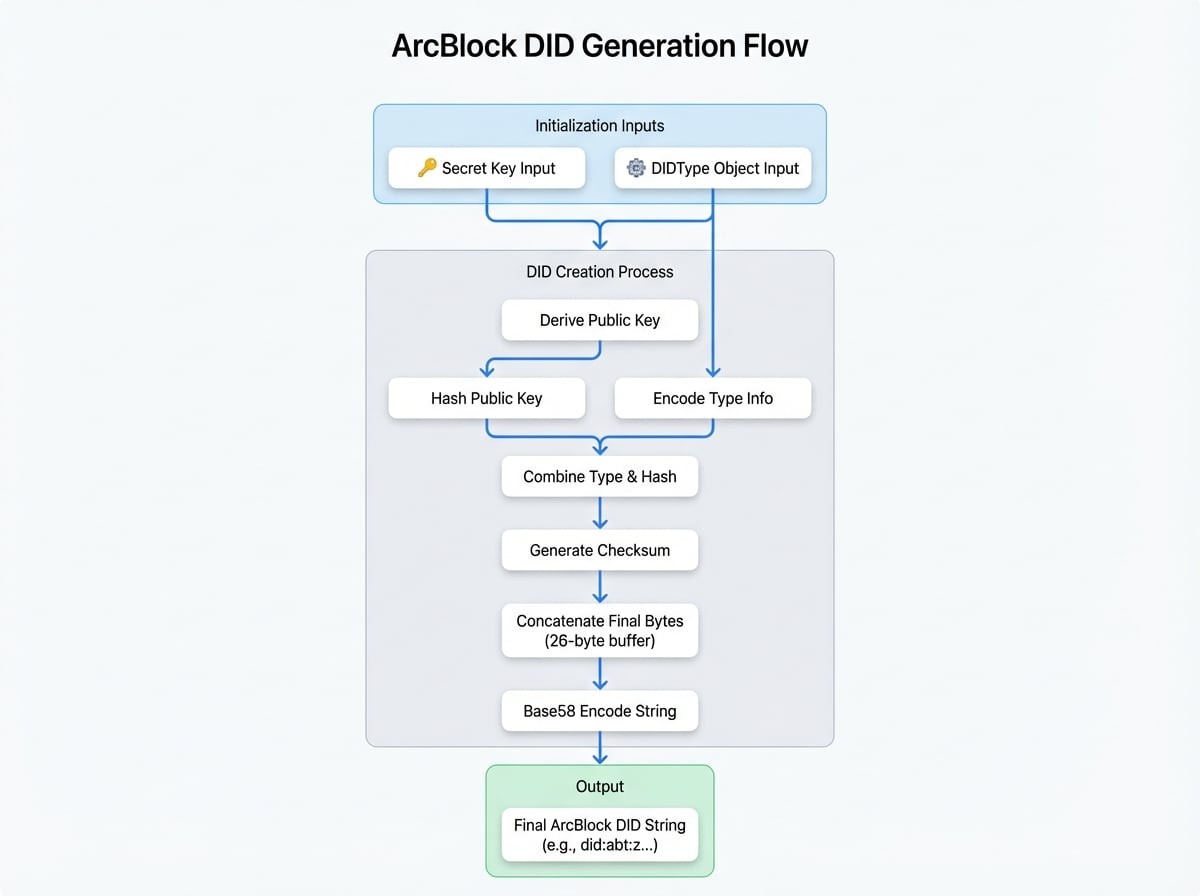
DID Generation Flow#
A DID is generated from a secret key and a DIDType object. The following diagram illustrates the process for a standard ArcBlock DID.
Ethereum-Compatible DIDs#
The library provides first-class support for Ethereum-compatible DIDs. These are standard Ethereum addresses, prefixed with 0x.
Unlike standard ArcBlock DIDs, an Ethereum DID does not encode its type information within the address itself. Instead, its type is inferred by its format. When the library encounters a valid Ethereum address, it automatically applies the 'ethereum' preset (ETHEREUM key type, KECCAK hash, BASE16 encoding). The library also handles EIP-55 checksum validation and generation to ensure interoperability with the broader Ethereum ecosystem.